ADDTECH | Ebike Electrical Components — Controller
By Addmotor | 29 February 2024 | 0 Comments
The ebike industry has boomed in recent years, thanks to the invention and widespread use of controllers. These controllers act as the brains of your electric bike, ensuring its smooth operation by connecting all electrical components. Essentially, they manage the overall functioning of the bike.
If you've ever been confused about Ebike controllers, in this detailed article, we'll cover everything you need to know about it.
This controller plays a crucial role in determining the power supplied to the motor, the motor's speed, torque output, and the efficient utilization of the battery. It's installed within an e-bike, connecting and coordinating all the key components like the motor, battery, pedal assistant, LCD display, sensors, and throttle to regulate the motor's speed, start, and stop functions.
While some controllers are solely responsible for accelerating the eBike or managing the pedal assist system, more advanced controllers, such as the EB2.0 controller from Addmotor, have evolved to feature a chip-type design.
This upgrade simplifies circuit systems, conserves board space, and enhances overall system stability. With a high-performance processor, the EB2.0 controller system now provides efficient, swift, and precise command control, ensuring a safe and enjoyable riding experience on your fat tire eBike.
Notably, the EB2.0 controller stands out for its innovative and future-proof design, adapting to changing rider needs and preferences. So, if you are looking for a controller that can make your e-bike more powerful, efficient, smoother, stable, and fun to ride, the EB2.0 controller from Addmotor is worth considering.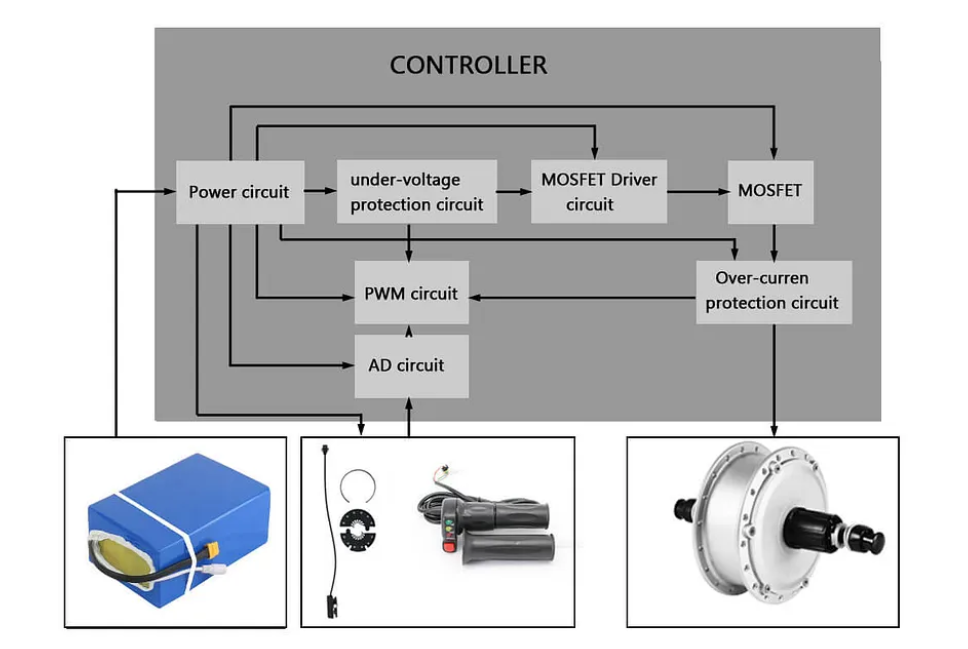
Image source: https://workholidayjiang.medium.com/what-do-you-know-about-electric-bike-controller-126f021e4f71
The electric bike controller serves as the central system managing all the essential functions of the ebike. It is made up of main chips, typically microcontrollers, and additional peripheral components like resistors, sensors, and MOSFETs.
It generally includes various circuits such as a PWM generator circuit, an AD (analog-to-digital) circuit, a power circuit, a power device driver circuit, and a signal acquisition and processing circuit. Additionally, the controller incorporates circuits for over-current and under-voltage protection. These components and circuits work together to manage and control the operation of the electric bike, ensuring proper functionality and safety.
Once the battery is connected, the controller supplies the working voltage to external devices, like the switch and headlight, through the power circuit, typically at +5V.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) generates a corresponding pulse waveform for the MOSFET drive circuit based on the input from the throttle or PAS (Pedal Assist System). The MOSFET drive circuit then manages the activation and deactivation of the MOSFET circuit, controlling the speed of the motor.
The under-voltage circuit is in place to safeguard the battery from excessive discharge when its voltage falls below the predetermined value set by the controller. During such instances, the PWM circuit halts the output.
Additionally, an over-current protection circuit is incorporated to restrict the operation of the controller, battery, and motor in cases of excessively high current. This circuit ensures that the system operates within safe limits and prevents potential damage.
The controller oversees crucial functions like pedaling activity, battery voltage, motor power, acceleration, and speed. It also manages pedal assist. Additionally, it displays relevant information like speed, distance, and battery level, and provides error codes and troubleshooting tips, acting as the central coordinator for a smooth riding experience.Types of E-Bike Controllers
A BLDC controller is designed for brushless DC motors, which are the most common type of motors used in electric bikes.
Brushless DC motors have permanent magnets, and they do not have brushes or commutators to switch the current direction. Instead, they rely on the controller to switch the current direction electronically, using a technique called electronic commutation.
They utilize three phases controlled by a set of keys, each phase being managed by at least two transistors, commonly referred to as key/MOSFET. These keys typically come in the range of 6, such as 6, 12, 18, etc.
The configuration and coordination of these elements play a crucial role in the precise control and efficient operation of brushless motors.
Pros
Apart from that, the brushed DC motor controllers are created using a connector and straightforward designs featuring a set of keys. These controllers are commonly used in small electric vehicles, including scooters, electric bicycles, pedelecs, ebikes, and other lightweight electric vehicles (EVs).
Pros
Pros
The chosen power mode not only influences the amount of assistance but also impacts the e-bike's speed and range. Riders can select power modes using a switch or button on the handlebar, or the controller can automatically adjust based on the prevailing riding conditions.
For non-programmable controllers, match the control voltage with the motor's voltage, and ensure the controller power is similar or slightly more than the motor power. Matching the voltages of the controller, motor, and battery enhances stability and prevents overheating.
The sine wave controller offers many advantages over a square wave controller, such as higher efficiency, lower noise, better torque, and smoother operation.
The Hall sensor configuration offers advantages such as low power consumption, increased stability, and a higher starting torque. On the other hand, a dual-mode controller is designed to continue functioning even if the Hall sensor is not working, ensuring a more reliable and uninterrupted operation.
So, with this in mind, prepare for new adventures, venture into unexplored territories, and relish the thrill of electric biking with a carefully chosen and effectively used e-bike controller.
If you've ever been confused about Ebike controllers, in this detailed article, we'll cover everything you need to know about it.

What is an Electric Bike Controller
An electric bike controller is a device that regulates the power flow from the battery to the motor and also communicates with other components. It's a circuit board housed in a sealed protective box with several connection wires sticking out.This controller plays a crucial role in determining the power supplied to the motor, the motor's speed, torque output, and the efficient utilization of the battery. It's installed within an e-bike, connecting and coordinating all the key components like the motor, battery, pedal assistant, LCD display, sensors, and throttle to regulate the motor's speed, start, and stop functions.
While some controllers are solely responsible for accelerating the eBike or managing the pedal assist system, more advanced controllers, such as the EB2.0 controller from Addmotor, have evolved to feature a chip-type design.
This upgrade simplifies circuit systems, conserves board space, and enhances overall system stability. With a high-performance processor, the EB2.0 controller system now provides efficient, swift, and precise command control, ensuring a safe and enjoyable riding experience on your fat tire eBike.
Notably, the EB2.0 controller stands out for its innovative and future-proof design, adapting to changing rider needs and preferences. So, if you are looking for a controller that can make your e-bike more powerful, efficient, smoother, stable, and fun to ride, the EB2.0 controller from Addmotor is worth considering.
How Ebike Controllers Work

Image source: https://workholidayjiang.medium.com/what-do-you-know-about-electric-bike-controller-126f021e4f71
The electric bike controller serves as the central system managing all the essential functions of the ebike. It is made up of main chips, typically microcontrollers, and additional peripheral components like resistors, sensors, and MOSFETs.
It generally includes various circuits such as a PWM generator circuit, an AD (analog-to-digital) circuit, a power circuit, a power device driver circuit, and a signal acquisition and processing circuit. Additionally, the controller incorporates circuits for over-current and under-voltage protection. These components and circuits work together to manage and control the operation of the electric bike, ensuring proper functionality and safety.
Once the battery is connected, the controller supplies the working voltage to external devices, like the switch and headlight, through the power circuit, typically at +5V.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) generates a corresponding pulse waveform for the MOSFET drive circuit based on the input from the throttle or PAS (Pedal Assist System). The MOSFET drive circuit then manages the activation and deactivation of the MOSFET circuit, controlling the speed of the motor.
The under-voltage circuit is in place to safeguard the battery from excessive discharge when its voltage falls below the predetermined value set by the controller. During such instances, the PWM circuit halts the output.
Additionally, an over-current protection circuit is incorporated to restrict the operation of the controller, battery, and motor in cases of excessively high current. This circuit ensures that the system operates within safe limits and prevents potential damage.
The controller oversees crucial functions like pedaling activity, battery voltage, motor power, acceleration, and speed. It also manages pedal assist. Additionally, it displays relevant information like speed, distance, and battery level, and provides error codes and troubleshooting tips, acting as the central coordinator for a smooth riding experience.
Types of E-Bike Controllers
1. BLDC Controller (Brushless DC Motor Controller)
A BLDC controller is designed for brushless DC motors, which are the most common type of motors used in electric bikes. Brushless DC motors have permanent magnets, and they do not have brushes or commutators to switch the current direction. Instead, they rely on the controller to switch the current direction electronically, using a technique called electronic commutation.
They utilize three phases controlled by a set of keys, each phase being managed by at least two transistors, commonly referred to as key/MOSFET. These keys typically come in the range of 6, such as 6, 12, 18, etc.
The configuration and coordination of these elements play a crucial role in the precise control and efficient operation of brushless motors.
Pros
♦ Exhibit high efficiency and operate within a broad speed range
♦ Effective and reliable, ensuring consistent performance over time.
♦ Operate noiseless and provide high torque
♦ Reduces wear and tear, resulting in a longer lifespan
♦ Eliminate electromagnetic interference
Cons
♦ The initial cost of purchasing a brushless motor controller is typically higher.
2. Brushed DC Motor Controller
A brushed DC motor controller is less common and less efficient than brushless DC motors. It also has permanent magnets, but they have brushes and commutators to switch the current direction mechanically. 2. Brushed DC Motor Controller
Apart from that, the brushed DC motor controllers are created using a connector and straightforward designs featuring a set of keys. These controllers are commonly used in small electric vehicles, including scooters, electric bicycles, pedelecs, ebikes, and other lightweight electric vehicles (EVs).
Pros
♦ Budget-friendly, requiring low production costs.
♦ Straightforward and simple to use.
♦ Feature a simple two-wire control system.
♦ Rebuildable to extend its lifespan.
Cons
♦ Compared to brushless DC motor controllers, they are less efficient.
♦ Regular maintenance is challenging
♦ Imposes a limit on the speed range.
♦ They produce irritating and noisy sounds
3. BLDC Controllers For Motors With Hall Sensors
A BLDC controller for motors with Hall sensors uses Hall sensors as the feedback mechanism to detect the position of the rotor and to switch the current accordingly. Hall sensors are located on the controller's circuit board, which plays a crucial role in monitoring and controlling rotation. These sensors are utilized to regulate the timing of power delivery, especially when it's necessary to initiate rotor movement.3. BLDC Controllers For Motors With Hall Sensors
Pros
♦ Boast a budget-friendly hardware setup.
♦ Utilize a simple and easy-to-understand algorithm.
♦ Enable higher revolutions per minute (RPM) for the motor.
Cons
♦ Less efficient due to the phase current waveform resembling square waves.
♦ Exhibit large torque ripples during operation.
Generate current noise during their functioning.
Functionality and Features of E-bike Controllers:
Power Modes
Power modes are the different levels of power that the controller can deliver to the motor, depending on the input from the throttle or the pedal assist sensor. It can range from eco-mode to normal mode and sport mode, offering different levels of power assistance.The chosen power mode not only influences the amount of assistance but also impacts the e-bike's speed and range. Riders can select power modes using a switch or button on the handlebar, or the controller can automatically adjust based on the prevailing riding conditions.
Speed Limiters
Speed limiters help in limiting the maximum speed that the e-bike can reach, depending on the legal regulations, safety considerations, or personal preferences of the rider. These limiters can be set by the controller, or by the rider using a display or a button on the handlebar.Battery Level Indicators
Battery level indicators show the remaining charge or capacity of the battery, depending on the voltage or the current of the battery. These indicators, often displayed on the e-bike controller’s screen, show the current battery level in a clear and easily understandable format. This allows you to keep track of your battery’s capacity and plan your rides accordingly. Battery level indicators can also show the charging status, the health status, or the temperature status of the battery.Error Codes and Troubleshooting
E-bike controllers come equipped with error codes and troubleshooting features to diagnose and resolve issues. When a problem arises, the controller displays a specific code corresponding to the particular issue. To address the issue, you can refer to the user manual or consult online resources to understand the meaning of the error code and take appropriate action for resolution.Key Factors in Choosing an Electric Bike Controller:
1. Compatibility with Your E-Bike
It's crucial to check the compatibility of the controller with your specific e-bike model before making a purchase. Different e-bike models may have unique requirements, and using an incompatible controller can lead to issues with fit or functionality. Ensuring compatibility ensures that the controller seamlessly integrates with your electric bike, preventing potential issues and ensuring optimal performance.2. Controller Voltage and Power
Controller voltage and power are the parameters that determine the maximum voltage and power that the controller can handle and deliver to the motor. Therefore, verify the power and voltage of the controller, especially if it comes with a motor.For non-programmable controllers, match the control voltage with the motor's voltage, and ensure the controller power is similar or slightly more than the motor power. Matching the voltages of the controller, motor, and battery enhances stability and prevents overheating.
3. Controller Current Rating
The controller current rating is the parameter that determines the maximum current that the controller can handle and deliver to the motor. When selecting a controller, ensure its current rating is lower than the battery's output current. Typically, a 9-MOSFET ebike controller has a maximum current rating of 25A, while a 15-MOSFET controller requires 40A, and a 6-MOSFET controller needs 18A.4. Phase and Battery Current
Phase and battery current determine the ratio of the current that flows through the motor phases and the battery wires, respectively. Ensure the phase current matches the motor current to avoid excessive heating. If the controller provides more current than required, it can lead to overheating. Aligning the phase current in the ebike's controller with the motor current promotes efficient operation.5. Controller Driving Type: Sine Wave or Square Wave Controller
The controller driving type determines the shape of the waveform that the controller sends to the motor phases. There are two main types of controller driving types: sine wave and square wave. A sine wave controller sends a smooth and continuous waveform that resembles a sine curve, while a square wave controller sends a choppy and discrete waveform that resembles a square shape.The sine wave controller offers many advantages over a square wave controller, such as higher efficiency, lower noise, better torque, and smoother operation.
6. Choose Among Dual-Mode Controller, Non-Hall Sensor, Or Hall Sensor Controller
If your E-bike motor is equipped with a Hall sensor, it's important to pair it with a controller designed to support Hall sensors or one that operates in dual mode. The Hall sensor detects the rotation of the motor, and based on the signals from the sensor, the controller generates the necessary voltage.The Hall sensor configuration offers advantages such as low power consumption, increased stability, and a higher starting torque. On the other hand, a dual-mode controller is designed to continue functioning even if the Hall sensor is not working, ensuring a more reliable and uninterrupted operation.
Conclusion
Ebike controllers serve as the control hub for your electric bike, giving you the ability to tap into the full power and capabilities of this amazing mode of transportation. By understanding the various types, features, and considerations, you can unleash the complete potential of your e-bike, ensuring a smooth and exciting ride.So, with this in mind, prepare for new adventures, venture into unexplored territories, and relish the thrill of electric biking with a carefully chosen and effectively used e-bike controller.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.Required fields are marked. *
Latest Stories




